U.S. Currency: Financial Benefit of Switching to a $1 Coin Is Unlikely, but Changing Coin Metal Content Could Result in Cost Savings
Fast Facts
The United States spent $1.3 billion to manufacture money in 2017. Is it possible to save money on manufacturing by changing the money itself?
In the past, Congress has discussed replacing $1 bills with coins or changing the metals used in the nickel.
Coins are usually cheaper than paper notes (bills) because they last longer. But $1 bills are lasting longer than ever—and we estimate it's cheaper to stick with them.
However, changing the metals in coins could save money without affecting how coins look or work. Because the Mint doesn't have the authority to make that change, we think Congress should consider providing that authority.

Highlights
What GAO Found
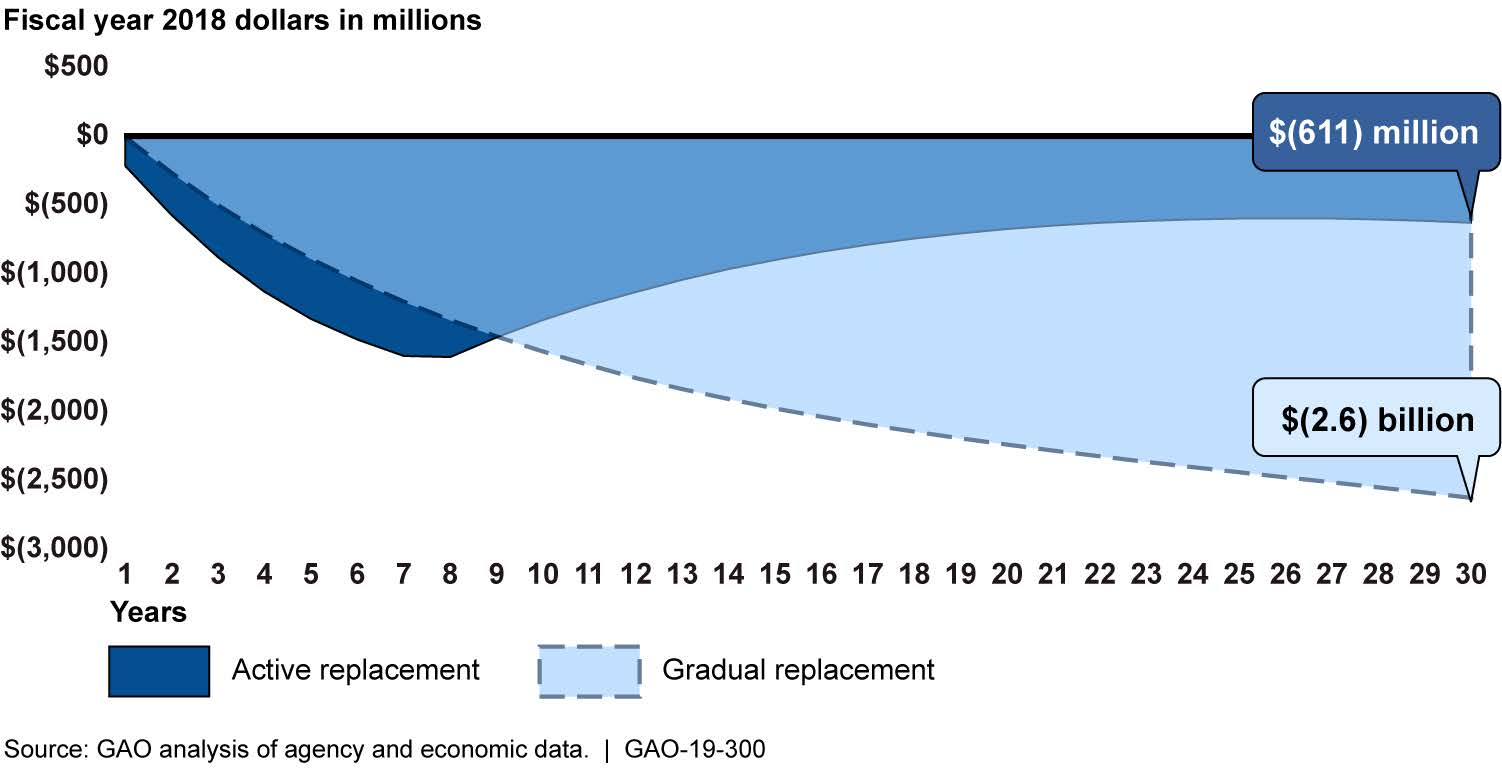
GAO's analysis found that replacing the $1 note with a $1 coin would likely result in a net loss to the government over 30 years. GAO found the government would incur a loss of about $611 million if notes were actively replaced and about $2.6 billion if $1 notes were replaced gradually (see figure). These simulations represent the first time GAO has found that replacing the $1 note with a $1 coin would result in a net loss to the government rather than a net benefit. GAO's estimates are based on current data and economic projections, which have changed over time. For example, the lifespan of the $1 note has more than doubled since a 2011 GAO analysis, from 3.3 years to 7.9 years, largely due to changes in note processing technology. Stakeholders generally identified few benefits from replacing $1 notes with $1 coins. Seven of 10 stakeholders GAO met with said that replacing the $1 note with a $1 coin would result in additional costs. For example, armored carriers told GAO that their transportation costs would increase because coins weigh more than notes.
Estimated Cumulative Present-Value Net Loss to the Government from Actively and Gradually Replacing $1 Notes with $1 Coins over 30 Years
The U.S. Mint estimates that it could save approximately $250 million over 10 years by suspending penny production and between $2 million and $9 million per year by changing the metal composition of the nickel. It also estimates that it could save about $74 million over 10 years by changing the metal composition of the dime and quarter. However, Federal Reserve officials and some stakeholders expressed concern about temporarily suspending the penny due to the potential for external effects, such as penny shortages. Stakeholders were unconcerned about changes to the nickel as long as the changes would not affect how the coin functioned, for example, in vending machines. Since Congress specifies in law which coins are made and their metal composition, the Mint has proposed legislation to enable the Secretary of the Treasury to change the metal content of coins as long as the weight or machine acceptance of the coins is unaffected. Without such authority, the Mint might not be producing coins as cost-effectively as possible.
Why GAO Did This Study
The U.S. spent about $1.3 billion in 2017 to produce, process, and circulate coins and paper notes for use in the economy. Since 2006, both the penny and nickel have cost more to make than their face value. Other countries have replaced notes with coins of the same value to reduce costs. Since 1990, GAO had estimated replacing the $1 note with a $1 coin would provide a benefit to the federal government.
GAO was asked to examine the potential cost savings to the government from making changes to currency. This report (1) estimates the net benefit to the government, if any, of replacing the $1 note with a $1 coin and selected stakeholders' views on this change; and (2) examines what is known about potential cost savings from suspending penny production and changing the metal composition of the nickel, and selected stakeholders' views on these changes. GAO conducted economic simulations of continued use of $1 notes and replacing notes with $1 coins, examined cost data from the U.S. Mint, and interviewed officials from the Federal Reserve, U.S. Mint and Bureau of Engraving and Printing as well as 10 selected stakeholders representing industries that could potentially be affected by currency changes.
Recommendations
Congress should consider taking steps to authorize the Secretary of the Treasury to adjust the metal content of circulating coins.
Matter for Congressional Consideration
| Matter | Status | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Congress should consider amending the law to provide the Secretary of the Treasury with the authority to alter the metal composition of circulating coins if the new metal compositions reduce the cost of coin production and do not affect the size, weight, appearance, or electromagnetic signature of the coins. (Matter for Consideration 1) | Neither of two bills (S.1228 and H.R. 2817) introduced in the 118th Congress that would have implemented GAO's March 2019 matter for consideration were enacted into law. As of January 24, 2025, such legislation has not been introduced in the 119th Congress. Without such action, the Mint might not be producing coins as cost-effectively as possible and would forego its estimated $9 to $16 million in cost savings annually. GAO will continue to monitor Congress's actions regarding this matter. |
