Defense Industrial Base: DOD Should Take Actions to Strengthen Its Risk Mitigation Approach
Fast Facts
More than 200,000 companies provide supplies, parts, and manufacturing for DOD's weapon systems. Risks to this defense industrial base include materials shortages, reliance on foreign suppliers, and more.
Various DOD offices and the military services monitor such risks and work to mitigate them. However, DOD doesn't have a robust strategy to mitigate risks or track progress department-wide.
Visibility over its department-wide efforts could help DOD determine whether the billions of dollars being spent are paying off. We recommended developing a robust strategy and measuring and reporting on DOD-wide industrial base risk mitigation efforts.

Highlights
What GAO Found
The Department of Defense's (DOD) Industrial Base Policy office does not yet have a consolidated and comprehensive strategy to mitigate risks to the industrial base—the companies that develop and manufacture technologies and weapon systems for DOD. The office is using a combination of four previously issued reports that were created for other requirements because it devoted its resources to completing other priorities. Collectively, the reports do not include several elements GAO has previously identified that would help DOD achieve results, evaluate progress, and ensure accountability (see figure).
Elements Not Fully Addressed in DOD's Industrial Base Strategy
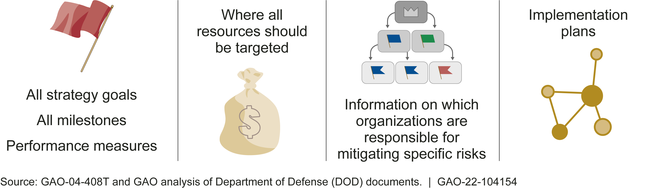
DOD must update its industrial base strategy following the submission of the next National Security Strategy Report, which is expected to be issued later in 2022. By including all elements in a consolidated strategy, DOD could better ensure that all appropriate organizations are working toward the same priorities, promoting supply chain resiliency, and supporting national security objectives.
DOD is carrying out numerous efforts to mitigate risks to the industrial base. This includes more than $1 billion in reported efforts under Navy submarine and destroyer programs and $125 million to sustain a domestic microelectronics manufacturer. However, DOD has limited insight into the effectiveness of these efforts and how much progress it has made addressing risks. For example:
- The Industrial Base Policy office and military services have not established enterprise-wide performance measures to monitor the aggregate effectiveness of DOD's mitigation efforts.
- DOD's annual Industrial Capabilities Reports do not include information about the progress the department has made in mitigating risks.
GAO's prior work on enterprise risk management establishes that agencies should monitor and report on the status and effectiveness of their risk mitigation efforts. Without key monitoring and reporting information, DOD and Congress do not have sufficient information to help determine whether industrial base risks have been mitigated and what additional resources or actions may be needed.
Why GAO Did This Study
A healthy defense industrial base that provides the capacity and capability to produce advanced weapon systems is critical to maintaining U.S. national security objectives. The U.S. industrial base currently consists of over 200,000 companies. Mitigating risks—such as reliance on foreign and single-source suppliers—is essential for DOD to avoid supply disruptions and ensure that the industrial base can meet current and future needs.
Since 2017, the White House has issued executive orders directing DOD and other agencies to assess risks to the defense industrial base and high priority supply chains such as semiconductors.
Congress also directed DOD to develop an analytical framework for mitigating risks and included a provision for GAO to review DOD's efforts. This report assesses (1) DOD's strategy for mitigating industrial base risks, and (2) the extent to which DOD is monitoring and reporting on its progress in mitigating risks. GAO analyzed DOD policies and reports and interviewed DOD officials.
Recommendations
GAO is making six recommendations, including that DOD develop a consolidated and comprehensive strategy to mitigate industrial base risks; develop and use enterprise-wide performance measures to monitor the aggregate effectiveness of its efforts; and report on its progress in mitigating risks. DOD generally concurred with the recommendations and identified some actions to address them.
Recommendations for Executive Action
| Agency Affected | Recommendation | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Department of Defense |
Priority Rec.
The Secretary of Defense should ensure that the National Technology and Industrial Base strategy is in a consolidated document and comprehensive, such as by including required resources and an implementation plan. (Recommendation 1) |
The Department of Defense (DOD) partially concurred with this recommendation and is taking steps to implement the recommendation. For example, in November 2023, the department issued its first National Defense Industrial Strategy, which lays out the long-term priorities for industrial base action. DOD officials anticipate that the department will issue corresponding implementation plans that will help with resource prioritization in November 2024. We will continue to track DOD's progress in this area.
|
| Department of Defense |
Priority Rec.
The Secretary of Defense should ensure that the Assistant Secretary of Defense for Industrial Base Policy, in coordination with the Industrial Base Council, develops and uses performance measures to monitor the aggregate effectiveness of mitigation efforts for DOD-wide industrial base risks. (Recommendation 2) |
DOD concurred with this recommendation and stated that it is aware of the need for performance measures to monitor the aggregate effectiveness of mitigation efforts for DOD-wide industrial base risks. It also stated that it is actively developing metrics aligned to the five focus areas in Executive Order 14017. DOD is making progress towards implementing this recommendation. For example, in February 2024 DOD officials provided us a set of metrics that senior leaders are using to monitor the health of the defense industrial base in the five focus areas, such as microelectronics, and energy storage and batteries. According to DOD officials, they are using an implementation plan related to the department's recently released National Defense Industrial Strategy to develop outcome metrics and performance measures to track progress for addressing industrial base risks. Officials anticipate completing the metrics and measures by July 2025. We will continue to track DOD's progress in this area.
|
| Department of Defense | The Secretary of the Air Force should ensure that the Assistant Secretary of the Air Force for Acquisition, Technology and Logistics develops and uses performance measures to monitor the aggregate effectiveness of mitigation efforts for Air Force and Space Force industrial base risks. (Recommendation 3) |
The Department of the Air Force concurred with this recommendation and identified several actions it plans to take through July 2026 to implement it. For example, the Air Force plans to participate on Assistant Secretary of Defense for Industrial Base Policy working groups to develop performance measures that can be aggregated to demonstrate DOD's effectiveness in mitigating risk. The Air Force is also consolidating information it has in various data systems to enable better monitoring and reporting on the risk mitigation measures.
|
| Department of Defense | The Secretary of the Army should ensure that the Assistant Secretary of the Army for Acquisition, Logistics, and Technology develops and uses performance measures to monitor the aggregate effectiveness of mitigation efforts for Army industrial base risks. (Recommendation 4) |
The Department of the Army concurred with this recommendation and identified several actions it plans to take through July 2026 to implement it. For example, the Army assessed its major commodity areas to identify the risks to the industrial base and map corrective actions to the identified risks. The Army plans to develop metrics to evaluate the effectiveness of its risk mitigation efforts, collect performance data, and then assess and evaluate the performance metrics to determine the impacts of its actions. The Army also plans to participate on Assistant Secretary of Defense for Industrial Base Policy working groups to develop performance measures that can be aggregated to demonstrate DOD's effectiveness in mitigating risk.
|
| Department of Defense | The Secretary of the Navy should ensure that the Assistant Secretary of the Navy for Research, Development, and Acquisition develops and uses performance measures to monitor the aggregate effectiveness of mitigation efforts for Navy and Marine Corps industrial base risks. (Recommendation 5) |
The Department of the Navy concurred with this recommendation and identified several actions it plans to take through September 2026 to implement it. For example, it plans to review the Navy's instructions and policies to determine applicability to current DOD requirements and initiatives for supply chain risk management. The Navy is also developing a supply chain illumination and program risk tool, as well as other measures that can be used for program reviews. Navy officials stated that they are working to establish measures of effectiveness to track industrial base supply chain risk within the Department of the Navy while remaining aligned with Assistant Secretary of Defense for Industrial Base Policy initiatives.
|
| Department of Defense | The Secretary of Defense should ensure that DOD reports its progress toward mitigating industrial base risks. For example, this information could be included in DOD's annual Industrial Capabilities Reports, which already include sector risk assessments. (Recommendation 6) |
DOD concurred with this recommendation and identified several actions it plans to take through July 2026 to implement it. For example, DOD plans for the military services to provide periodic updates to senior leaders on their actions and metrics for executing initiatives included in the National Defense Industrial Strategy Implementation Plan. DOD also plans to publish periodic updates on its effort, but did not provide any details on how, when, and where this would occur.
|
