High-Risk Series: Urgent Action Needed to Address Critical Cybersecurity Challenges Facing the Nation
Fast Facts
Federal IT systems and the nation's critical infrastructure are often under threat. Federal agencies reported over 30,000 IT security incidents in FY 2022.
We reported on the government's 4 major cybersecurity challenges:
Establishing a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy and performing effective oversight
Securing federal systems and information
Protecting the cybersecurity of critical infrastructure
Protecting privacy and sensitive data
Since 2010, we've made 1,610 recommendations to address issues in these areas. Federal agencies have implemented 1,043 of our recommendations, but 567 remain unimplemented as of May 2024.

Highlights
What GAO Found
Risks to our nation's essential technology systems are increasing. Threats to these systems can come from a variety of sources and vary in terms of the types and capabilities of the actors, their willingness to act, and their motives. Federal agencies reported 30,659 information security incidents to the Department of Homeland Security's United States Computer Emergency Readiness Team in fiscal year 2022. Such attacks could result in serious harm to human safety, national security, the environment, and the economy.
Concerted action among the federal government and its nonfederal partners is critical to mitigating the risks posted by cyber-based threats. Recognizing the growing threat, the federal government urgently needs to take action to address the four major cybersecurity challenges and 10 associated critical actions (see figure).
Figure: Four Major Cybersecurity Challenges and 10 Associated Critical Actions
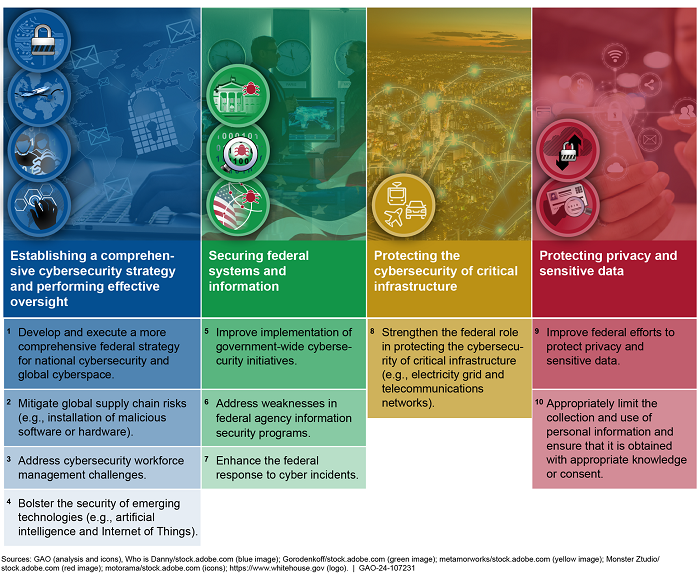
Since 2010, GAO has made 1,610 recommendations in public reports that address the four cybersecurity challenge areas. As of May 2024, federal agencies had implemented 1,043 of these recommendations; 567 remain unimplemented. Until these recommendations are fully implemented, federal agencies will be limited in their ability to:
- provide effective oversight of critical government-wide initiatives, mitigate global supply chain risks, address challenges with cybersecurity workforce management, and better ensure the security of emerging technologies;
- improve implementation of government-wide cybersecurity initiatives, address weaknesses in federal agency information security programs, and enhance the federal response to cyber incidents;
- mitigate cybersecurity risks for key critical infrastructure systems and their data; and
- protect private and sensitive data entrusted to them.
Why GAO Did This Study
Federal agencies and the nation's critical infrastructures depend on technology systems to carry out fundamental operations and to process, maintain, and report vital information. The security of these systems and data is also important to safeguarding individual privacy and protecting the nation's security, prosperity, and well-being.
GAO first designated information security as a government-wide High-Risk area in 1997. This was expanded to include protecting the cybersecurity of critical infrastructure in 2003 and the privacy of personally identifiable information in 2015.
In 2018, GAO reported that the federal government needed to address four major cybersecurity challenges: (1) establishing a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy and performing effective oversight, (2) securing federal systems and information, (3) protecting the cybersecurity of critical infrastructure, and (4) protecting privacy and sensitive data. Within these four challenges are 10 actions essential to successfully dealing with the serious cybersecurity threats facing the nation.
GAO's objective was to describe the challenges facing the federal government in ensuring the cybersecurity of the nation and the progress it has made in addressing these challenges. To do so, GAO identified its recent public reports related to each challenge and summarized relevant findings from this work. GAO also determined the implementation status of relevant recommendations made in these reports. Further, GAO identified its ongoing and upcoming work covering each of the 10 critical actions needed to address the four major cybersecurity challenges.
For more information, contact Marisol Cruz Cain at (202) 512-5017 or cruzcainm@gao.gov.
