Gas Stoves: Risks and Safety Standards Related to Products and Ventilation
Fast Facts
Millions of Americans use gas stoves, which can produce emissions that may pose health risks.
In this Q&A, we reviewed how industry, standards development organizations, and federal agencies are working to improve gas stove safety. Some of these groups have initiated research and safety efforts. For example, there are ongoing studies of indoor air quality and research projects for improving vent hoods and exhaust fans.
Coordinating the standards for stoves and ventilation—which are handled by different standards organizations—is one of a few challenges we identified.
Robust collaboration on the challenges could further improve gas stove safety.

Highlights
What GAO Found
Gas stoves pose certain health and safety risks, due in part to potentially harmful emissions, including nitrogen dioxide, but there is ongoing debate about the extent of their impact on human health. These risks can be mitigated with ventilation (see figure below).
Figure: External Ventilation of Gas Stove Emissions of Health Concern
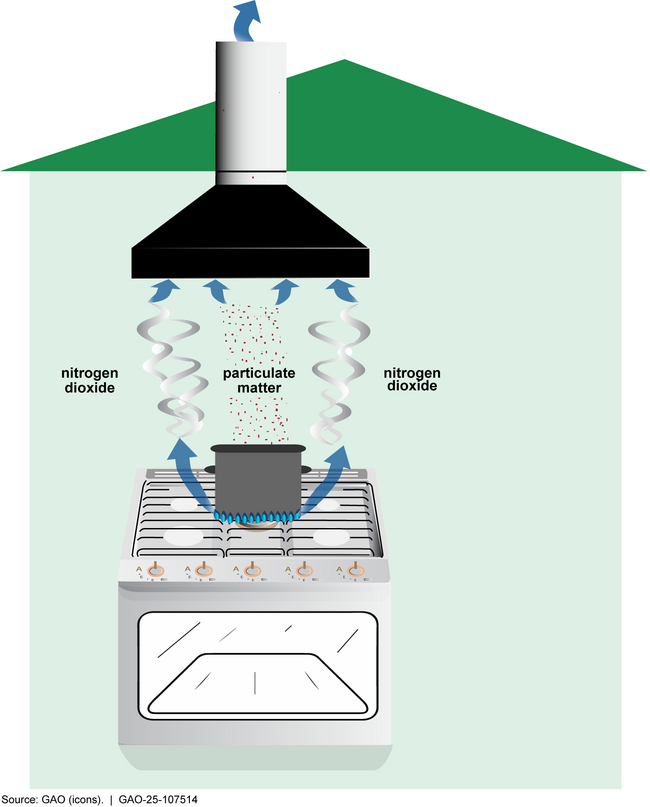
Note: Gas stove cooking produces particulate matter through the combustion process as well as some cooking processes (such as pan frying). In addition to nitrogen dioxide and particulate matter, gas stove cooking emits carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide, and it can also emit methane, benzene, and other gases. In this report, we focus on nitrogen dioxide, particulate matter, and carbon monoxide because they are described by the Environmental Protection Agency as major pollutants from gas stoves. The amount of carbon monoxide produced is usually not hazardous. However, if gas stoves are not working properly or are used incorrectly, dangerous levels of carbon monoxide can result in a space with inadequate ventilation. Additionally, the effectiveness of ventilation systems such as range hoods varies in capturing and exhausting the emissions. As a result, some of the emissions can remain in the room or home.
Why GAO Did This Study
Millions of Americans use gas stoves—that is, gas ovens, cooktops, and ranges. While voluntary standards for gas stoves are developed and updated regularly through consensus-based processes to help protect users, researchers and others have raised concerns about the potential risks from emissions associated with these appliances. However, there is disagreement about the extent of linkage between the emissions produced by gas stoves and certain health issues. The Senate Report accompanying the Financial Services and General Government Appropriations Bill of 2024 includes a provision for GAO to report on actions taken by industry and the federal government to improve gas stove safety.
For this work, we interviewed and collected information from industry, testing organizations, academia, health organizations, and government sources relevant to the safety of gas stoves. Concerning standards, we contacted several standards development organizations with efforts related to the safety of gas stoves and analyzed documentation related to safety improvements of gas stove products and kitchen ventilation.
For more information, contact Alicia Puente Cackley at (202) 512-8678 or cackleya@gao.gov.
