Medicaid Providers: CMS Oversight Should Ensure State Implementation of Screening and Enrollment Requirements
Fast Facts
States must screen and enroll health care providers in Medicaid according to federal and state rules. These rules are designed to exclude providers who don’t meet minimum standards, which can help prevent fraud, waste, and abuse. Congress established new federal rules in 2010 and 2016, yet officials we spoke with in 5 of 7 states said they haven’t implemented all of them.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services oversees states’ administration of Medicaid, but it doesn’t have a complete picture of state compliance with the new rules. We recommended that it expand its oversight.
The Medicaid program is on our High Risk List.
Summary of Provider Screening Activities for Medicaid Enrollment
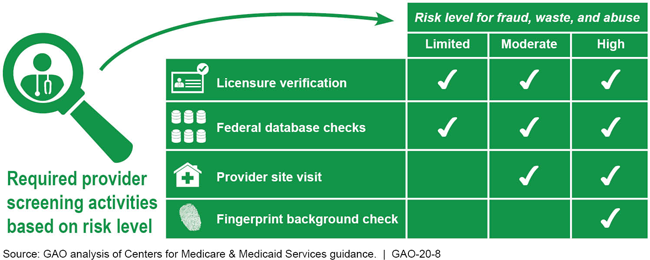
Chart showing fraud, waste, and abuse risk levels for provider activities
Highlights
What GAO Found
Officials from seven selected states that GAO interviewed described challenges they faced implementing new Medicaid provider screening and enrollment requirements, established by the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA) in 2010 and the 21st Century Cures Act in 2016. These challenges included establishing procedures for risk-based screenings, using federal databases and collecting required information, and screening an increased volume of providers. Due in part to these challenges, officials from five of the seven selected states told GAO they had not implemented certain requirements. For example, one state plans to launch its new information technology system, which automates screenings, before it will enroll providers under contract with managed care organizations, as required under these laws.
Summary of Provider Screening Activities for Medicaid Enrollment
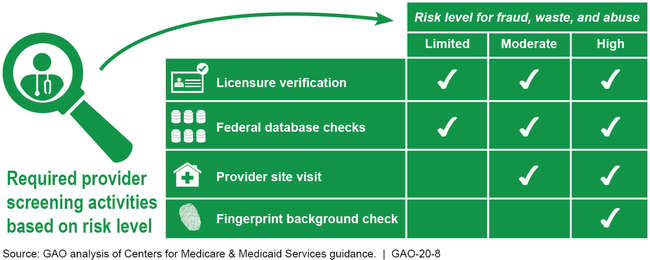
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS)—the federal agency that oversees Medicaid—supports states' implementation of new requirements with tailored optional consultations, such as CMS contractor site visits that examine the extent of states' implementation. Yet, because these are optional, states that need support might not participate, and CMS would not have information on those states. CMS uses other methods to oversee states' compliance, such as, the Payment Error Rate Measurement (PERM) process for estimating improper payments, and focused program integrity reviews.
PERM. This process assesses states' compliance with provider screening and enrollment requirements, but does not assess compliance for all providers and all requirements, and occurs once every 3 years.
Focused program integrity reviews. These reviews examine specific areas in Medicaid, like state compliance with provider screening and enrollment requirements, but have not been done in all states. CMS conducted reviews in 39 states in fiscal years 2014 through 2018.
Collectively, CMS's oversight methods do not provide it with comprehensive and timely reviews of states' implementation of the provider screening and enrollment requirements or the remediation of deficiences. As a result, CMS lacks assurance that only eligible providers are participating in the Medicaid program.
Why GAO Did This Study
A crucial component of protecting the integrity of the Medicaid program is ensuring that only eligible providers participate in Medicaid. States' non-compliance with provider screening and enrollment requirements contributed to over a third of the $36.3 billion estimated improper payments in Medicaid in 2018. To improve the integrity of the Medicaid program, PPACA and the 21st Century Cures Act established new requirements for screening and enrolling providers and expanded enrollment to include additional provider types.
In this report, GAO (1) describes challenges states faced implementing provider screening and enrollment requirements; and (2) examines CMS support for and oversight of states' implementation of these requirements. GAO reviewed federal laws and CMS guidance. GAO also reviewed CMS documents, including reports resulting from CMS oversight activities published from 2014 through 2018 for seven states. These states were selected based on their use of CMS's contractor site visits, among other things. GAO also interviewed officials from CMS and the seven selected states.
Recommendations
GAO recommends that CMS (1) expand its review of states' implementation of provider screening and enrollment requirements to include states that have not participated in optional consultations; and (2) for states not fully compliant with the requirements, annually monitor the progress of those states' implementation. The Department of Health and Human Services, the department that houses CMS, concurred with both recommendations.
Recommendations for Executive Action
| Agency Affected | Recommendation | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services | The Administrator of CMS should expand its review of states' implementation of the provider screening and enrollment requirements to include states that have not made use of CMS's optional consultations. Similar to CMS's contractor site visits, such reviews should include any necessary steps to address areas of noncompliance for all types of enrolled providers, including those under contract with managed care organizations. (Recommendation 1) |
CMS concurred with our recommendation. In September 2024, CMS awarded a 5-year contract to conduct in-person visits to states and assess their compliance with provider screening and enrollment and ownership disclosure requirements. According to the contract statement of work, the contractor will conduct visits in up to five states each year, and CMS will identify the states. According to CMS officials, CMS will select states based on factors, including states' most recent Payment Error Rate Measurement error rate; single audit findings; self-reported levels of compliance with provider screening, enrollment, and disclosure requirements; and whether and when a state had previously been visited by CMS. This contract builds upon CMS's prior actions to assess states' compliance with provider screening and enrollment requirements. For example, in our October 2019 report, we found that 17 states had undergone a multi-day site visit to assess compliance with all provider screening and enrollment requirements. Since our report, at least four additional states had also undergone such site-visits. CMS has also continued to take other steps to monitor states' compliance with provider screening and enrollment requirements, including providing technical assistance; communicating regularly with states via phone calls and emails; and updating guidance for completing the Annual Managed Care report to begin collecting some information on provider screening and enrollment. Further, CMS has continued to help states meet provider screening and enrollment requirements through activities, such as offering services to compare providers enrolled in states' Medicaid programs with providers previously screened for Medicare and enhancing states' access to certain data files used to conduct screens. In light of the new contract and the agency's continued efforts, we are closing this recommendation as implemented.
|
| Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services | The Administrator of CMS should annually monitor progress toward addressing any areas of noncompliance related to the provider screening and enrollment requirements for any state with one or more corrective action plans. (Recommendation 2) |
HHS concurred with our recommendation. In February 2025, agency officials told us that CMS's review of errors identified through the Payment Error Rate Measure (PERM) program, which include errors related to provider screening and enrollment, involves stakeholders from across the agency. For PERM errors related to provider enrollment, CMS's Provider Enrollment Oversight Group reviews enrollment issues and recommendations for corrective action plans, and provides technical assistance. CMS also told us it documents reviews, such as email communications, and stores this information on internal share sites. To fully address this recommendation, CMS needs to demonstrate that it assesses, on an annual basis, areas of non-compliance with provider screening and enrollment requirements, including those not identified through the PERM, for any states with one or more corrective actions. We will continue to monitor CMS's progress.
|
